Introduction
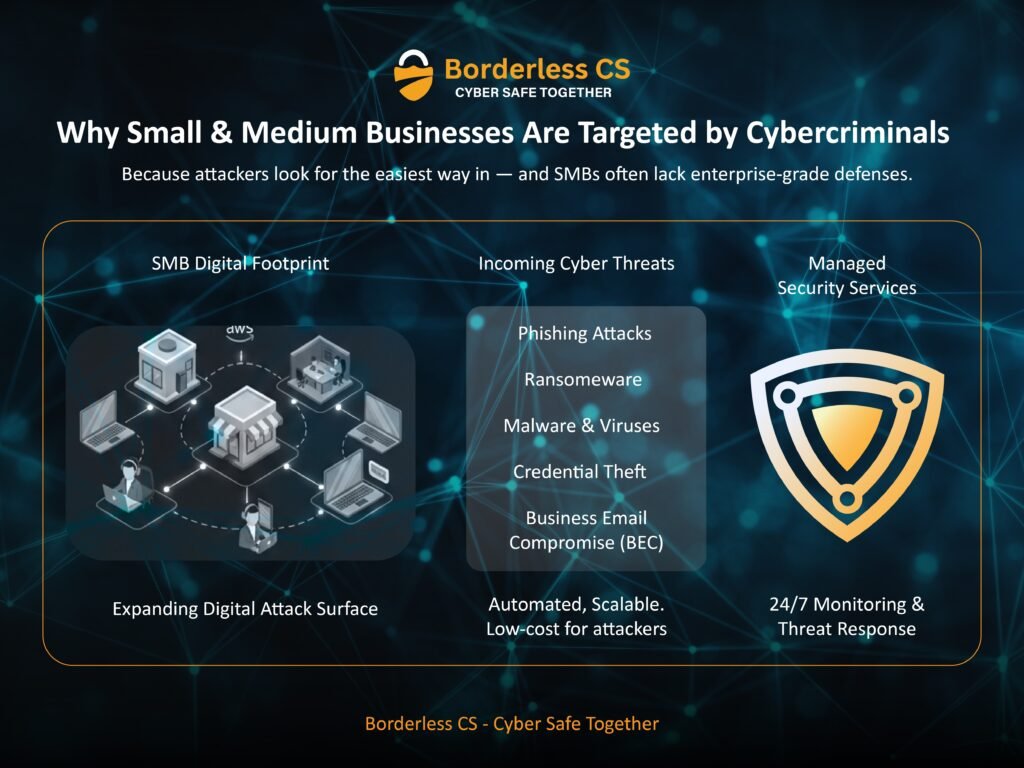
Small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) are increasingly becoming prime targets for cybercriminals. Contrary to popular belief, hackers don’t only target large corporations—SMBs are often seen as easier targets due to limited security budgets and lack of dedicated IT teams.
In this guide, we explore cybersecurity for SMBs, the most common threats, essential protection strategies, affordable tools, and best practices to safeguard your business in today’s digital environment.
Why Cybersecurity Matters for SMBs
Many SMBs assume they are “too small” to be attacked. However:
- Cyberattacks on SMBs are rising globally
- Data breaches can lead to financial loss
- Reputation damage can impact long-term trust
- Regulatory penalties may apply for data exposure
For small businesses, a single breach can cause severe operational disruption.
Common Cyber Threats Facing SMBs
🎣 Phishing Attacks
Fraudulent emails or messages trick employees into revealing passwords or financial information.
🦠 Ransomware
Malware encrypts business data and demands payment for its release.
🔓 Weak Passwords
Poor password practices make systems easy to compromise.
🌐 Unsecured Networks
Public Wi-Fi or poorly configured routers can expose sensitive data.
👤 Insider Threats
Employees (intentionally or accidentally) can create vulnerabilities.
Essential Cybersecurity Measures for SMBs
🔐 Implement Strong Password Policies
- Use complex passwords
- Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA)
- Utilize password managers
Trusted security providers like LastPass and 1Password offer secure solutions for teams.
🛡️ Install Endpoint Protection
Antivirus and endpoint security tools protect devices from malware and ransomware.
Popular options include:
- Bitdefender
- Norton
🔄 Regular Software Updates
Outdated software often contains vulnerabilities. Ensure:
- Operating systems are updated
- Applications are patched
- Firewalls are properly configured
📊 Data Backup Strategy
Implement automated backups:
- Store copies offline or in the cloud
- Test backups regularly
- Use encrypted storage solutions
Cloud services from providers like Microsoft and Google offer secure storage options.
👩🏫 Employee Training & Awareness
Human error is a major cause of breaches. Train employees to:
- Identify phishing emails
- Use secure passwords
- Report suspicious activity
- Avoid downloading unknown files
Cyber awareness training significantly reduces risk.
Affordable Cybersecurity Tools for SMBs
Many SMB-friendly solutions offer scalable pricing:
- Cloud-based firewalls
- Managed security services (MSSPs)
- Security monitoring software
- Automated patch management tools
These tools provide enterprise-level security without enterprise-level costs.
Regulatory & Compliance Considerations
Depending on industry and location, SMBs may need to comply with:
- Data protection laws
- Payment security standards
- Industry-specific regulations
Failing to comply can result in fines and legal consequences.
Incident Response Plan for SMBs
Every business should have a response strategy that includes:
- Identifying the breach
- Containing affected systems
- Notifying stakeholders
- Restoring data from backups
- Investigating and preventing future attacks
Preparation reduces downtime and financial impact.
The Future of Cybersecurity for SMBs
Emerging trends include:
- AI-powered threat detection
- Zero-trust security models
- Cloud-native security solutions
- Automated compliance monitoring
As cyber threats become more advanced, SMBs must adopt proactive and scalable security strategies.
Conclusion
Cybersecurity for SMBs is no longer optional—it’s a business necessity. While small and medium-sized businesses may not have the resources of large corporations, affordable and effective security solutions are widely available.
By combining technology, employee awareness, and strong policies, SMBs can significantly reduce their risk and operate confidently in the digital world.
FAQs (SEO-Optimized)
Q: Are small businesses really targeted by hackers?
Yes. SMBs are often targeted because attackers assume weaker security defenses.
Q: What is the biggest cybersecurity risk for SMBs?
Phishing attacks and ransomware are among the most common threats.
Q: How much should an SMB spend on cybersecurity?
Spending depends on size and risk level, but investing in basic protections is far less expensive than recovering from a breach.